A silent evil Ovarian Cancer
The ovaries are two small-large organs in women. Located internally at the level of the pelvis and have the function of the secretion of female hormones and egg production.
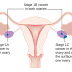
The ovaries are covered with epithelial cells. When these cells begin to reproduce abnormally, leading to different types of cancer that attack the ovaries.
The risk of developing ovarian cancer increases as women grow old, having more chances to develop after age 50.
The causes of ovarian cancer are poorly understood. But there is talk that hormonal and genetic factors play a role.
Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors
Risk factors are those conditions that predispose a greater proportion of women to develop ovarian cancer, among them are:- Family History: Women with first-degree relativeness (like mother or sister) who have suffered from ovarian cancer have an increased risk of this cancer. The risk of developing this cancer is greater if in the family if someone has or had breast cancer or colon cancer.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially for women who have entered menopause and are over 50 years.
- A number of children: Interestingly, studies have shown that cancer is more prevalent in those who have not had children than women that have had and the more children a lower risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Having had other cancers: If a woman also has or has had breast cancer or colon cancer, she has to face twice the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Fertility treatments: Fertility treatments that increase ovulation are related to ovarian cancer. In fact, women who undergo such treatments are far more likely to suffer from this cancer than the rest of the population.
Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
Ovarian cancer is a silent evil; its symptoms are very mild and not very distinguishable from low-risk disease and usually arrive when the cancer is advanced.Ovarian Cancer General symptoms include:
1. Abdominal pain
2. Abdominal swelling 3. Pelvic pressure
4. The quick feeling of fullness after eating little
5. Indigestion
6. Nausea
7. Diarrhea
8. Frequent urination
9. Loss of appetite
10. Weight loss or gain without justification
11. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
12. Fatigue
13. Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
14. Menstrual changes
However, routine tests such as pelvic examination can help diagnose it, but for the examiner, even the most experienced, it is difficult to feel abnormal lumps in the ovaries or close to them.
The Pap smear, despite being such a good agent in cervical cancer screening, does not work to detect ovarian cancer. If Pap test results show the presence of ovarian cancer it means that ovarian cancer is advanced and has also gone to the cervix.
There is a posttest that is more reliable to detect ovarian cancer, which is: the transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 test.
Thus, both examinations, transvaginal ultrasound, and CA-125 are complementary to each other.
These two tests are performed in women at high risk, such as those with a family history of ovarian cancer or who are highly suspected, because of their symptoms, that they have ovarian cancer.
In general, MOST patients undergo surgery. In surgery removal of the ovaries, uterus, cervix and fallopian tubes are made. This intervention is known as “hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy "
If ovarian cancer has moved to other areas it is also removed by a surgeon.
After surgery, the patient will go under chemotherapy treatment. Intravenous involves the injection of anticancer drugs to complete the removal of cancer.
At the completion of chemotherapy, surgery is done to verify the observation that cancer has been eliminated.
Radiation therapy is more localized, it damages malignant treated cells in the area. It is up to specialists to continue that type of therapy after the operation.
4. The quick feeling of fullness after eating little
5. Indigestion
6. Nausea
7. Diarrhea
8. Frequent urination
9. Loss of appetite
10. Weight loss or gain without justification
11. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
12. Fatigue
13. Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
14. Menstrual changes
Ovarian Cancer Diagnose
The early diagnose of ovarian cancer is really difficult because its symptoms often appear as benign diseases.However, routine tests such as pelvic examination can help diagnose it, but for the examiner, even the most experienced, it is difficult to feel abnormal lumps in the ovaries or close to them.
The Pap smear, despite being such a good agent in cervical cancer screening, does not work to detect ovarian cancer. If Pap test results show the presence of ovarian cancer it means that ovarian cancer is advanced and has also gone to the cervix.
There is a posttest that is more reliable to detect ovarian cancer, which is: the transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 test.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is an ultrasound that places a small instrument into the vagina. This is a test to find ovarian mass, but not to distinguish if it is or not cancer. To find out, the doctor has to take biopsies or tissue samples.
- The CA-125is a protein that increases in the blood of many women with ovarian cancer. The problem with this test is that other conditions that have nothing to do with cancer also increase the protein as well. Healthy people can also have high levels of CA-125.
Thus, both examinations, transvaginal ultrasound, and CA-125 are complementary to each other.
These two tests are performed in women at high risk, such as those with a family history of ovarian cancer or who are highly suspected, because of their symptoms, that they have ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Once you have Been Diagnosed with cancer, the doctor makes the decision to proceed with the best treatment whether surgery, chemotherapy, establishment or combinations of them.In general, MOST patients undergo surgery. In surgery removal of the ovaries, uterus, cervix and fallopian tubes are made. This intervention is known as “hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy "
If ovarian cancer has moved to other areas it is also removed by a surgeon.
After surgery, the patient will go under chemotherapy treatment. Intravenous involves the injection of anticancer drugs to complete the removal of cancer.
At the completion of chemotherapy, surgery is done to verify the observation that cancer has been eliminated.
Radiation therapy is more localized, it damages malignant treated cells in the area. It is up to specialists to continue that type of therapy after the operation.
How to Know Ovarian Cancer Signs Symptoms and Treatment
 Reviewed by Health Tips
on
September 18, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Health Tips
on
September 18, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Health Tips
on
September 18, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Health Tips
on
September 18, 2019
Rating:







![45 Fantastic Ways to Burn Calories [UPDATED] 45 Fantastic Ways to Burn Calories [UPDATED]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh2-30L6DkeMS8Tp3tZbZM6lB_URwEjqQXmWsn0S7NMPb5AXseyMCSLc8IYgvcy0yYKC0xdrlElxKE9fTkcN4qkXFw8tkvFeH8ic0Zlak6Zm-vrir-U5quwteRoycZCgQ1fj_ejBZSggZ0/s72-c/45+Fantastic+Ways+to+Burn+Calories+%255BUPDATED%255D.png)

![7 Most Side Effects of Energy Drinks [Beware] 7 Most Side Effects of Energy Drinks [Beware]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi2p8G1Cmu7qYTgsiSSA5DlLkufDxaHmTvCkYbTfOO7htNdFUqW8iUaN0OeZ8BPETpOh9E7a7_-bRMJA6nJWBXklkgXmV9zfm7LWrIDu6QCZfa4JJEW7BNAEk7reK3fZ9CIHQ6XL81-l4g/s72-c/7+Most+Side+Effects+of+Energy+Drinks+%255BBeware%255D.jpg)

No comments: